How Deep Should You Bury A Dog Safely: Proper Depth
So, you’re wondering, “How deep should you bury a dog?” The recommended burial depth for a dog is generally between 3 to 6 feet from the surface to the top of the grave. This depth is crucial for several important reasons, ensuring the safety and dignity of your beloved pet.
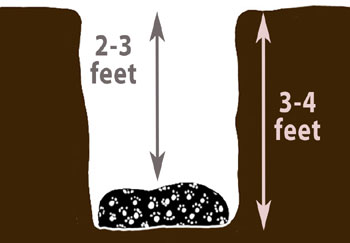
Image Source: www.dfordog.co.uk
Why Proper Burial Depth Matters
When a beloved pet passes away, especially a dog, the decision of how to lay them to rest is a deeply personal and often emotional one. For many, burying their pet at home offers a sense of comfort and connection. However, simply digging a hole and placing your pet inside isn’t always the best or safest approach. The burial depth for pets is a critical consideration, impacting everything from environmental protection to preventing unwanted attention from scavengers.
Fathoming the Importance of Burial Depth for Pets
The dog burial depth guidelines are not arbitrary; they are based on practical needs and environmental considerations. A grave that is too shallow can lead to several issues. It can be disturbed by other animals, such as foxes, coyotes, or even stray dogs, who might be attracted by the scent. This can be incredibly distressing for grieving pet owners. Furthermore, shallow graves can be affected by weather conditions, such as erosion from heavy rain, potentially exposing the remains.
On the other hand, a grave that is too deep might be unnecessarily difficult to dig, especially in certain soil types or if you have physical limitations. The aim is to find a balance that ensures security, prevents environmental contamination, and is manageable for the pet owner.
Decoding Appropriate Depth for Dog Grave
The appropriate depth for dog grave is a topic that deserves careful attention. While 3 to 6 feet is a widely accepted range, this can be influenced by a few factors:
- Size of the Dog: A larger dog will require a slightly larger and potentially deeper grave than a smaller dog, simply to accommodate their body and allow for adequate soil cover.
- Local Soil Conditions: Hard, rocky soil can make digging deeper more challenging. Conversely, sandy soil might require a deeper grave to prevent collapse.
- Local Regulations: This is a very important point and will be discussed in more detail later. Some areas have specific pet burial depth regulations that must be followed.
Ensuring Pet Burial Depth Safety
Pet burial depth safety is paramount. A grave that is deep enough (3-6 feet) serves several safety functions:
- Deterrent to Scavengers: As mentioned, deeper graves make it significantly harder for animals to dig up the remains. This protects your pet’s body and prevents the spread of potential pathogens.
- Environmental Protection: Proper burial depth helps to ensure that the decomposition process does not negatively impact groundwater. As a body decomposes, it releases fluids. A sufficient layer of soil acts as a natural filter, breaking down these substances and preventing them from contaminating water sources.
- Prevents Accidental Disturbance: A well-covered grave is less likely to be accidentally dug up by children playing in the yard or by landscaping activities.
Grave Depth for Deceased Dog: What the Experts Say
When considering the grave depth for deceased dog, it’s helpful to look at recommendations from veterinary professionals and animal welfare organizations. They often emphasize the importance of a minimum depth to ensure dignity and public health. The general consensus points to the 3-6 foot range as a good guideline for most situations.
- Minimum Depth: Aim for at least 3 feet of soil covering the pet.
- Ideal Depth: 4 to 6 feet provides an extra layer of security and environmental protection.
Legal Depth for Pet Burial: Navigating Regulations
The question of legal depth for pet burial is crucial for anyone considering home burial. While many people are allowed to bury pets on their own property, there are often regulations in place to protect public health and the environment.
- Local Ordinances: It is absolutely essential to check with your local municipal or county authorities before you dig. Zoning laws, health department regulations, and even homeowner association rules can dictate where and how you can bury a pet. These regulations might specify a minimum recommended burial depth dog or prohibit home burial altogether in certain areas.
- Water Sources: Regulations often prohibit burial within a certain distance of wells, streams, or other water bodies to prevent contamination.
- Zoning: In some urban or suburban areas, zoning laws might prevent the burial of animals on residential property.
Failure to comply with local laws could result in fines or the requirement to exhume and re-bury the pet. Always err on the side of caution and get the necessary information.
Recommended Burial Depth Dog: A Practical Guide
When you are planning to bury your dog at home, following the recommended burial depth dog is key. Here’s a step-by-step approach to ensure you are doing it correctly:
Step 1: Check Local Regulations
As emphasized, this is the very first and most important step. Call your local animal control, health department, or city hall. Ask specifically about regulations concerning pet burial depth regulations and home burial.
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Location
Select a spot in your yard that is:
- Away from Water Sources: Ensure it’s a safe distance from wells, septic systems, rivers, or lakes.
- Not a High-Traffic Area: Avoid places where children play, where you frequently walk, or where future construction might occur.
- Free of Underground Utilities: Call 811 or your local utility locating service to mark any underground lines before you dig.
Step 3: Dig the Grave
- Measure Your Dog: Get an estimate of your dog’s length and width.
- Determine Depth: Aim for the 3-6 foot range from the bottom of the grave to the surface level. This means you’ll need to dig a hole that is roughly 3-6 feet deep.
- Widen Appropriately: Make the grave wide enough to comfortably place your dog in it.
- Consider Soil: If the soil is very hard, you might need to rent a tiller or a small digging machine. If the soil is very loose, you might need to reinforce the sides of the grave.
Step 4: Prepare the Pet
- Wrap Your Dog: It’s common practice to wrap your pet’s body in a biodegradable material. This could be a thick cotton sheet, a wool blanket, or a purpose-made pet burial shroud. Avoid plastic materials, as they hinder decomposition.
- Optional: Pet Casket: Some owners choose a small pet casket, which can be made of wood or other biodegradable materials. Ensure the casket fits comfortably within the grave.
Step 5: Lower Your Pet into the Grave
- Gently place your dog into the prepared grave.
- If you are using a casket, carefully lower it into the hole.
Step 6: Backfill the Grave
- Begin filling the grave with the soil you excavated.
- Layering: It’s good practice to put a layer of soil over the pet first, then continue filling.
- Compacting: Gently compact the soil as you go to prevent excessive settling later.
- Mounding: It’s natural for the grave to sink slightly as the soil settles and decomposition occurs. You can create a slight mound over the grave to accommodate this.
Step 7: Mark the Grave (Optional)
Many owners choose to mark their pet’s resting place with a headstone, a special rock, or a memorial plaque.
Burying a Dog at Home Depth: Key Considerations
When burying a dog at home depth is a primary concern, think about these factors:
- Sufficient Cover: The minimum of 3 feet of soil cover is crucial. This ensures that the scent is masked and that animals cannot easily access the remains.
- Soil Stability: If you live in an area with very loose soil, digging to 6 feet might be safer to prevent the grave from collapsing.
- Frost Line: In colder climates, you may need to dig below the frost line to prevent the grave from being disturbed by ground freezing and thawing cycles, although this is less of a concern for deeper graves.
Pet Burial Depth Regulations: A Deeper Dive
Understanding pet burial depth regulations can vary significantly from one place to another. Here’s a breakdown of common regulations and considerations:
- Minimum Depth: Many jurisdictions specify a minimum depth, often around 3 feet.
- Maximum Depth: While less common, some areas might have a maximum depth to prevent overly extensive excavation.
- Distance from Property Lines: Regulations might require a certain distance from property boundaries.
- Proximity to Water: As mentioned, this is a critical factor. A common rule might be to bury at least 100 feet away from any water source.
- Type of Material: Some regulations might discourage or prohibit the use of non-biodegradable materials in the grave.
Table: Factors Influencing Pet Burial Depth
| Factor | Impact on Burial Depth |
|---|---|
| Dog Size | Larger dogs require slightly more space and adequate soil cover. |
| Soil Type | Loose soil may need deeper graves for stability; hard soil makes digging harder. |
| Local Regulations | Dictate minimum/maximum depths, distances from water, and permitted locations. |
| Scavenger Activity | Higher local scavenger populations may warrant deeper graves (towards the 6-foot end). |
| Environmental Concerns | Preventing groundwater contamination is a primary driver for sufficient depth. |
| Climate | Frost lines can be a consideration in very cold regions, though less critical for deeper graves. |
Alternatives to Home Burial
If home burial isn’t feasible due to regulations, space constraints, or personal preference, there are other respectful options:
- Pet Cemeteries: These facilities provide dedicated burial plots and often offer various memorialization options. They handle all the logistical aspects, including proper depth.
- Cremation: Pet cremation is a popular choice. You can opt for communal cremation or private cremation, where you receive your pet’s ashes back. The ashes can then be kept in an urn, scattered in a meaningful place, or buried in a shallow grave or memorial garden.
- Coping Stones/Markers: Even if you choose cremation, you might opt to bury the urn or ashes in your yard, using a shallow marker. In this case, the depth requirements are less stringent as there is no biological decomposition.
Addressing Common Concerns About Burial Depth
How deep to bury a pet safely is a recurring question. The safety aspect is multifaceted:
- Personal Safety: Ensure the grave is stable and you do not injure yourself while digging.
- Animal Safety: Prevent other animals from digging up the grave.
- Environmental Safety: Protect water sources from contamination.
A grave dug to the appropriate depth for dog grave addresses all these safety concerns effectively.
FAQ Section: Your Questions Answered
Q1: What is the minimum recommended burial depth for a dog?
A1: The minimum recommended burial depth for a dog is generally 3 feet of soil covering the body.
Q2: Can I bury my dog in a plastic coffin?
A2: It is generally not recommended to use plastic materials for pet burial. Biodegradable materials like cotton or wool are preferred to allow for natural decomposition and to comply with environmental regulations. Always check local pet burial depth regulations regarding materials.
Q3: Who should I contact to find out about local burial laws for pets?
A3: You should contact your local municipal or county government, specifically the health department, animal control, or zoning office.
Q4: Is it legal to bury a pet in my backyard?
A4: In many areas, it is legal to bury a pet in your backyard, provided you follow local pet burial depth regulations and zoning laws. Always confirm with your local authorities first.
Q5: What if my dog is very large? Do I need to dig deeper?
A5: While the general depth range of 3-6 feet is suitable, a larger dog might require a slightly wider grave. The emphasis remains on achieving adequate soil cover (at least 3 feet) over the entire body.
Q6: What are the risks of burying a pet too shallow?
A6: The main risks of a shallow grave include disturbance by scavengers, potential exposure of remains due to erosion, and a higher risk of environmental contamination if decomposition fluids reach the surface or groundwater.
Q7: Are there specific guidelines for the grave depth for a deceased dog in terms of decomposition?
A7: The 3-6 foot depth is primarily for preventing external disturbances and environmental contamination. The rate of decomposition is influenced by many factors, including temperature, soil type, and moisture, but the depth ensures the process occurs without causing public health or environmental issues.
Q8: How can I ensure the burial site remains undisturbed in the future?
A8: Choosing a location away from high-traffic areas and marking the grave appropriately can help. For long-term peace of mind, consider a pet cemetery if home burial is a concern.
Q9: What is the difference between pet burial depth guidelines and pet burial depth regulations?
A9: Guidelines are recommendations based on best practices, while regulations are legal requirements set by local authorities. It is always important to adhere to the legal regulations.
Q10: What is the recommended burial depth for a cat versus a dog?
A10: The depth recommendations are generally the same for cats and dogs, focusing on achieving adequate soil cover (typically 3-6 feet). The size of the animal is more of a factor in the width and length of the grave rather than the depth itself.
Final Thoughts on Respectful Farewell
Laying a pet to rest is one of the most challenging aspects of pet ownership. By carefully considering the dog burial depth guidelines, understanding legal depth for pet burial, and ensuring pet burial depth safety, you can provide your loyal companion with a dignified and respectful final resting place. Always prioritize checking local regulations to ensure you are compliant, and remember that a well-prepared grave is a testament to the love and bond you shared.
